MedicalDemo4
Repository source: MedicalDemo4
Description¶
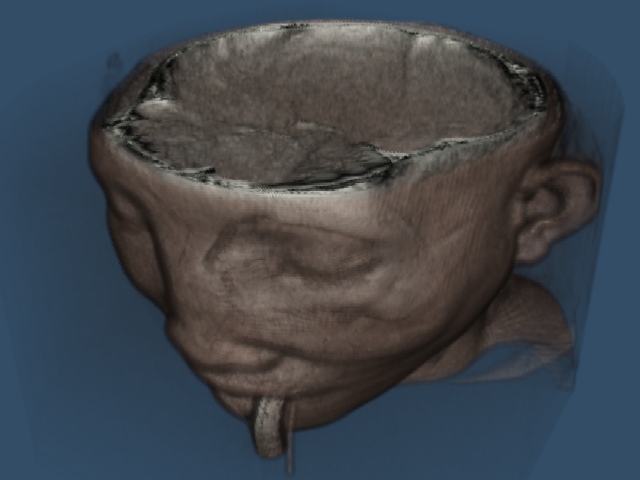
Volume rendering of the dataset.
Usage
MedicalDemo4 FullHead.mhd
Note
This original source code for this example is here.
Info
The example uses src/Testing/Data/FullHead.mhd which references src/Testing/Data/FullHead.raw.gz.
Question
If you have a question about this example, please use the VTK Discourse Forum
Code¶
MedicalDemo4.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
import vtkmodules.vtkInteractionStyle
# noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
import vtkmodules.vtkRenderingOpenGL2
# noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
import vtkmodules.vtkRenderingVolumeOpenGL2
from vtkmodules.vtkCommonColor import vtkNamedColors
from vtkmodules.vtkCommonDataModel import vtkPiecewiseFunction
from vtkmodules.vtkIOImage import vtkMetaImageReader
from vtkmodules.vtkRenderingCore import (
vtkColorTransferFunction,
vtkRenderWindow,
vtkRenderWindowInteractor,
vtkRenderer,
vtkVolume,
vtkVolumeProperty
)
from vtkmodules.vtkRenderingVolume import vtkFixedPointVolumeRayCastMapper
def main():
colors = vtkNamedColors()
file_name = get_program_parameters()
colors.SetColor('BkgColor', [51, 77, 102, 255])
# Create the renderer, the render window, and the interactor. The renderer
# draws into the render window, the interactor enables mouse- and
# keyboard-based interaction with the scene.
ren = vtkRenderer()
ren_win = vtkRenderWindow()
ren_win.AddRenderer(ren)
iren = vtkRenderWindowInteractor()
iren.SetRenderWindow(ren_win)
# The following reader is used to read a series of 2D slices (images)
# that compose the volume. The slice dimensions are set, and the
# pixel spacing. The data Endianness must also be specified. The reader
# uses the FilePrefix in combination with the slice number to construct
# filenames using the format FilePrefix.%d. (In this case the FilePrefix
# is the root name of the file: quarter.)
reader = vtkMetaImageReader()
reader.SetFileName(file_name)
# The volume will be displayed by ray-cast alpha compositing.
# A ray-cast mapper is needed to do the ray-casting.
volume_mapper = vtkFixedPointVolumeRayCastMapper()
volume_mapper.SetInputConnection(reader.GetOutputPort())
# The color transfer function maps voxel intensities to colors.
# It is modality-specific, and often anatomy-specific as well.
# The goal is to one color for flesh (between 500 and 1000)
# and another color for bone (1150 and over).
volume_color = vtkColorTransferFunction()
volume_color.AddRGBPoint(0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
volume_color.AddRGBPoint(500, 240.0 / 255.0, 184.0 / 255.0, 160.0 / 255.0)
volume_color.AddRGBPoint(1000, 240.0 / 255.0, 184.0 / 255.0, 160.0 / 255.0)
volume_color.AddRGBPoint(1150, 1.0, 1.0, 240.0 / 255.0) # Ivory
# The opacity transfer function is used to control the opacity
# of different tissue types.
volume_scalar_opacity = vtkPiecewiseFunction()
volume_scalar_opacity.AddPoint(0, 0.00)
volume_scalar_opacity.AddPoint(500, 0.15)
volume_scalar_opacity.AddPoint(1000, 0.15)
volume_scalar_opacity.AddPoint(1150, 0.85)
# The gradient opacity function is used to decrease the opacity
# in the 'flat' regions of the volume while maintaining the opacity
# at the boundaries between tissue types. The gradient is measured
# as the amount by which the intensity changes over unit distance.
# For most medical data, the unit distance is 1mm.
volume_gradient_opacity = vtkPiecewiseFunction()
volume_gradient_opacity.AddPoint(0, 0.0)
volume_gradient_opacity.AddPoint(90, 0.5)
volume_gradient_opacity.AddPoint(100, 1.0)
# The VolumeProperty attaches the color and opacity functions to the
# volume, and sets other volume properties. The interpolation should
# be set to linear to do a high-quality rendering. The ShadeOn option
# turns on directional lighting, which will usually enhance the
# appearance of the volume and make it look more '3D'. However,
# the quality of the shading depends on how accurately the gradient
# of the volume can be calculated, and for noisy data the gradient
# estimation will be very poor. The impact of the shading can be
# decreased by increasing the Ambient coefficient while decreasing
# the Diffuse and Specular coefficient. To increase the impact
# of shading, decrease the Ambient and increase the Diffuse and Specular.
volume_property = vtkVolumeProperty()
volume_property.SetColor(volume_color)
volume_property.SetScalarOpacity(volume_scalar_opacity)
volume_property.SetGradientOpacity(volume_gradient_opacity)
volume_property.SetInterpolationTypeToLinear()
volume_property.ShadeOn()
volume_property.SetAmbient(0.4)
volume_property.SetDiffuse(0.6)
volume_property.SetSpecular(0.2)
# The vtkVolume is a vtkProp3D (like a vtkActor) and controls the position
# and orientation of the volume in world coordinates.
volume = vtkVolume()
volume.SetMapper(volume_mapper)
volume.SetProperty(volume_property)
# Finally, add the volume to the renderer
ren.AddViewProp(volume)
# Set up an initial view of the volume. The focal point will be the
# center of the volume, and the camera position will be 400mm to the
# patient's left (which is our right).
camera = ren.GetActiveCamera()
c = volume.GetCenter()
camera.SetViewUp(0, 0, -1)
camera.SetPosition(c[0], c[1] - 400, c[2])
camera.SetFocalPoint(c[0], c[1], c[2])
camera.Azimuth(30.0)
camera.Elevation(30.0)
# Set a background color for the renderer
ren.SetBackground(colors.GetColor3d('BkgColor'))
# Increase the size of the render window
ren_win.SetSize(640, 480)
ren_win.SetWindowName('MedicalDemo4')
# Interact with the data.
iren.Start()
def get_program_parameters():
import argparse
description = 'Read a volume dataset and displays it via volume rendering.'
epilogue = '''
Derived from VTK/Examples/Cxx/Medical4.cxx
'''
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=description, epilog=epilogue,
formatter_class=argparse.RawDescriptionHelpFormatter)
parser.add_argument('filename', help='FullHead.mhd.')
args = parser.parse_args()
return args.filename
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()