CurvaturesDemo
Repository source: CurvaturesDemo
Description¶
How to get the Gaussian and Mean curvatures of a surface.
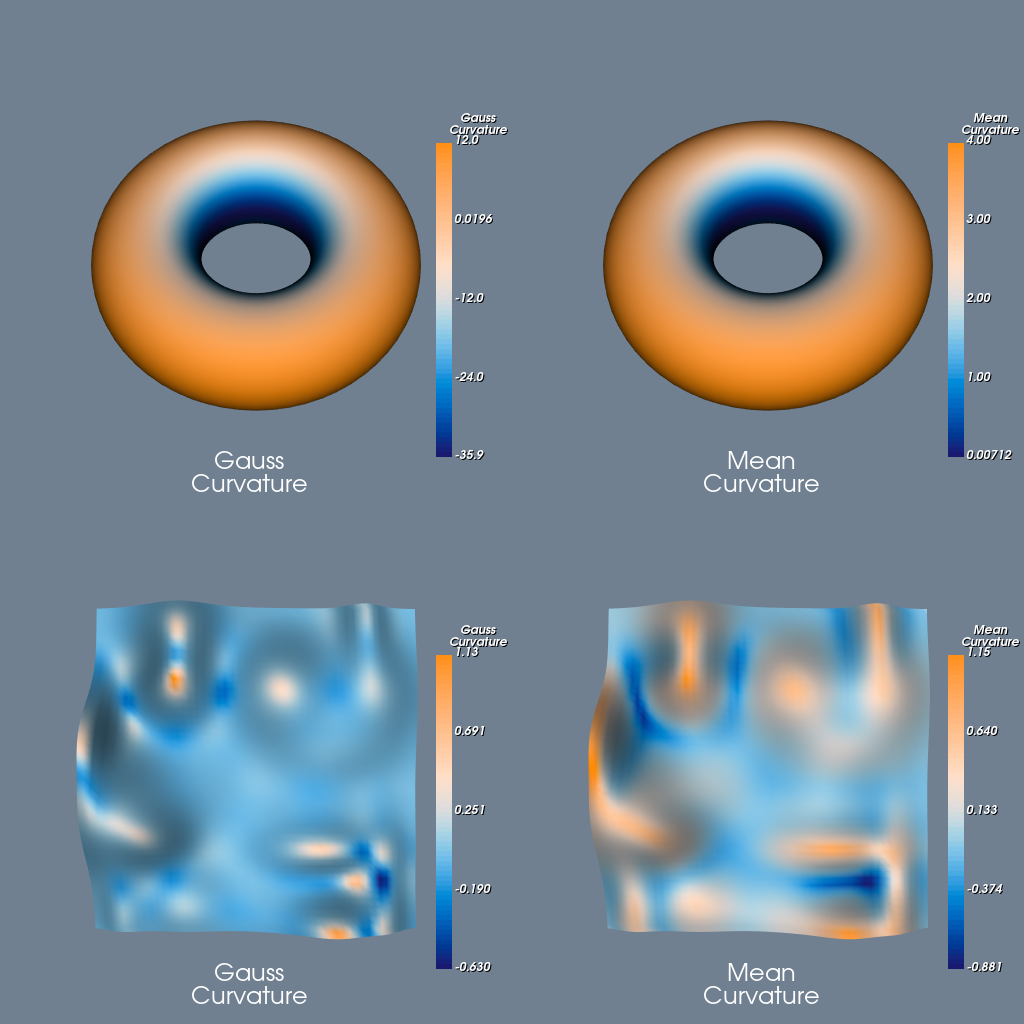
Two different surfaces are used in this demonstration with each surface coloured according to its Gaussian and Mean curvatures.
-
The first surface is a superquadric surface, this demonstrates the use of extra filters that are needed to get a nice smooth surface.
-
The second surface is a parametric surface, in this case the surface has already been triangulated so no extra processing is necessary.
In order to get a nice coloured image, a vtkColorTransferFunction has been used to generate a set of colours for the vtkLookupTable tables. We have used a diverging colour space. Because of the symmetry of the ranges selected for the lookup tables, the white colouration represents a midpoint value whilst the blue represents values less than the midpoint value and orange represents colours greater than the midpoint value.
In the case of the Random Hills Gaussian curvature surface, this colouration shows the nature of the surface quite nicely. The blue areas are saddle points (negative Gaussian curvature) and the orange areas have a positive Gaussian curvature.
In the case of the mean curvature the blue colouration represents negative curvature perpendicular to one of the principal axes.
Other languages
See (Python)
Question
If you have a question about this example, please use the VTK Discourse Forum
Code¶
CurvaturesDemo.cxx
/*
The purpose of this is to demonstrate how to get the Gaussian and Mean
curvatures of a surface.
Two different surfaces are used in this demonstration with each
surface coloured according to its Gaussian and Mean curvatures.
The first surface is a superquadric surface, this demonstrates the use
of extra filters that are needed to get a nice smooth surface.
The second surface is a parametric surface, in this case the surface
has already been triangulated so no extra processing is necessary.
In order to get a nice coloured image, a vtkColorTransferFunction has
been used to generate a set of colours for the vtkLookUp tables. We
have used a diverging colour space. Because of the symmetry of the
ranges selected for the lookup tables, the white colouration
represents a midpoint value whilst the blue represents values less
than the midopoint value and orange represents colours greater than the
midpoint value.
In the case of the Random Hills Gaussian Curvature surface, this
colouration shows the nature of the surface quite nicely. The blue
areas are saddle points (negative Gaussian curvature) and the orange
areas have a positive Gaussian curvature.
In the case of the mean curvature the blue colouration is representing
negative curvature perpendicular to one of the principal axes.
This example also demonstrates the use of std::vector and the linking
of the elements of the vector together to form a pipeline.
*/
#include <vtkActor.h>
#include <vtkActor2D.h>
#include <vtkCleanPolyData.h>
#include <vtkColorTransferFunction.h>
#include <vtkCurvatures.h>
#include <vtkFeatureEdges.h>
#include <vtkInteractorStyleTrackballCamera.h>
#include <vtkLookupTable.h>
#include <vtkNamedColors.h>
#include <vtkNew.h>
#include <vtkParametricFunctionSource.h>
#include <vtkParametricRandomHills.h>
#include <vtkPointData.h>
#include <vtkPolyDataMapper.h>
#include <vtkRenderWindow.h>
#include <vtkRenderWindowInteractor.h>
#include <vtkRenderer.h>
#include <vtkScalarBarActor.h>
#include <vtkScalarBarRepresentation.h>
#include <vtkScalarBarWidget.h>
#include <vtkSmartPointer.h>
#include <vtkSuperquadricSource.h>
#include <vtkTextActor.h>
#include <vtkTextMapper.h>
#include <vtkTextProperty.h>
#include <vtkTextRepresentation.h>
#include <vtkTextWidget.h>
#include <vtkTransform.h>
#include <vtkTransformFilter.h>
#include <vtkTriangleFilter.h>
#include <vtkVersion.h>
#include <vtk_cli11.h>
#include <vtk_fmt.h>
// clang-format off
#include VTK_FMT(fmt/format.h)
// clang-format on
// vtkGenerateIds was introduced in VTK build version 20240504
#if VTK_BUILD_VERSION >= 20240504
#define USE_USE_GENERATE_IDS
#include <vtkGenerateIds.h>
#else
#include <vtkIdFilter.h>
#endif
// #include <algorithm>
// #include <array>
// #include <cctype>
// #include <cmath>
// #include <cstdlib>
// #include <functional>
// #include <iomanip>
// #include <iostream>
// #include <iterator>
// #include <map>
// #include <numeric>
#include <set>
// #include <sstream>
namespace fs = std::filesystem;
namespace {
//! Adjust curvatures along the edges of the surface.
/*!
* This function adjusts curvatures along the edges of the surface by replacing
* the value with the average value of the curvatures of points in the
* neighborhood.
*
* Remember to update the vtkCurvatures object before calling this.
*
* @param source - A vtkPolyData object corresponding to the vtkCurvatures
* object.
* @param curvatureName: The name of the curvature, "Gauss_Curvature" or
* "Mean_Curvature".
* @param epsilon: Curvature values less than this will be set to zero.
* @return
*/
void AdjustEdgeCurvatures(vtkPolyData* source, std::string const& curvatureName,
double const& epsilon = 1.0e-08);
vtkSmartPointer<vtkLookupTable> GetDivergingLut();
vtkSmartPointer<vtkLookupTable> GetDivergingLut1();
typedef std::map<std::string, std::array<double, 2>> TTextPosition;
typedef std::map<std::string, TTextPosition> TTextPositions;
struct ScalarBarProperties
{
vtkSmartPointer<vtkNamedColors> colors;
// The properties needed for scalar bars.
vtkSmartPointer<vtkLookupTable> lut;
// These are in pixels.
std::map<std::string, int> maximumDimensions{{"width", 100}, {"height", 260}};
std::string titleText{""};
std::string labelFormat{"{:0.2f}"};
int number_of_labels{5};
// Orientation vertical=true, horizontal=false.
bool orientation{true};
// Horizontal and vertical positioning.
// These are the defaults, don't change these.
TTextPosition defaultV = {{"p", {0.85, 0.2}}, {"p2", {0.1, 0.6}}};
TTextPosition defaultH = {{"p", {0.10, 0.1}}, {"p2", {0.7, 0.1}}};
// Modify these as needed.
TTextPosition positionV = {{"p", {0.85, 0.2}}, {"p2", {0.1, 0.6}}};
TTextPosition positionH = {{"p", {0.10, 0.1}}, {"p2", {0.7, 0.1}}};
};
/** Make a scalar bar widget.
*
* @param scalar_bar_properties - The lookup table, title name, maximum
* dimensions in pixels and position.
* @param textProperty - The properties for the title.
* @param labelTextProperty - The properties for the labels.
* @param ren - The vtkRenderer.
* @param iren - The vtkInteractor.
* @return The scalar bar widget.
*/
vtkNew<vtkScalarBarWidget>
MakeScalarBarWidget(ScalarBarProperties& scalarBarProperties,
vtkTextProperty* textProperty,
vtkTextProperty* labelTextProperty, vtkRenderer* ren,
vtkRenderWindowInteractor* iren);
/**
* Get viewport positioning information for a vector of names.
*
* Note: You must include vtkSystemIncludes.h to get these defines:
* VTK_TEXT_LEFT 0, VTK_TEXT_CENTERED 1, VTK_TEXT_RIGHT 2,
* VTK_TEXT_BOTTOM 0, VTK_TEXT_TOP 2
*
* @param names - The vector of names.
* @param justification - Horizontal justification of the text.
* @param vertical_justification - Vertical justification of the text.
* @param width - Width of the bounding_box of the text in screen coordinates.
* @param height - Height of the bounding_box of the text in screen
* coordinates.
* @return A map of positioning information.
*/
TTextPositions
GetTextPositions(std::vector<std::string> const& names,
int const justification = VTK_TEXT_LEFT,
int const vertical_justification = VTK_TEXT_BOTTOM,
double const width = 0.96, double const height = 0.1);
/** Convert a string to title case.
*
* @param input - The string to convert.
* @return The string converted to title case.
*/
std::string Title(const std::string& input);
} // namespace
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CLI::App app{"Display the Gaussian and Mean curvatures of two"
"surfaces with adjustments for edge effects."};
CLI11_PARSE(app, argc, argv);
vtkNew<vtkNamedColors> colors;
// We are going to handle two different sources.
// The first source is a superquadric source.
vtkNew<vtkSuperquadricSource> torus;
torus->SetCenter(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
torus->SetScale(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
torus->SetPhiResolution(64);
torus->SetThetaResolution(64);
torus->SetThetaRoundness(1);
torus->SetThickness(0.5);
torus->SetSize(0.5);
torus->SetToroidal(1);
// Rotate the torus towards the observer (around the x-axis).
vtkNew<vtkTransform> torusT;
torusT->RotateX(55);
vtkNew<vtkTransformFilter> torusTF;
torusTF->SetInputConnection(torus->GetOutputPort());
torusTF->SetTransform(torusT);
// The quadric is made of strips, so pass it through a triangle filter as
// the curvature filter only operates on polys.
vtkNew<vtkTriangleFilter> tri;
tri->SetInputConnection(torusTF->GetOutputPort());
// The quadric has nasty discontinuities from the way the edges are generated
// so let's pass it though a CleanPolyDataFilter and merge any points which
// are coincident, or very close.
vtkNew<vtkCleanPolyData> cleaner;
cleaner->SetInputConnection(tri->GetOutputPort());
cleaner->SetTolerance(0.005);
cleaner->Update();
// The next source will be a parametric function.
vtkNew<vtkParametricRandomHills> rh;
vtkNew<vtkParametricFunctionSource> rhFnSrc;
rhFnSrc->SetParametricFunction(rh);
rhFnSrc->Update();
std::map<int, vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>> sources;
for (auto i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
std::string curvatureName;
if (i < 2)
{
vtkNew<vtkCurvatures> cc;
cc->SetInputConnection(cleaner->GetOutputPort());
if (i % 2 == 0)
{
cc->SetCurvatureTypeToGaussian();
curvatureName = "Gauss_Curvature";
}
else
{
cc->SetCurvatureTypeToMean();
curvatureName = "Mean_Curvature";
}
cc->Update();
AdjustEdgeCurvatures(cc->GetOutput(), curvatureName);
sources[i] = cc->GetOutput();
}
else
{
vtkNew<vtkCurvatures> cc;
cc->SetInputConnection(rhFnSrc->GetOutputPort());
if (i % 2 == 0)
{
cc->SetCurvatureTypeToGaussian();
curvatureName = "Gauss_Curvature";
}
else
{
cc->SetCurvatureTypeToMean();
curvatureName = "Mean_Curvature";
}
cc->Update();
AdjustEdgeCurvatures(cc->GetOutput(), curvatureName);
sources[i] = cc->GetOutput();
}
}
std::map<int, std::string> curvatures{
{0, {"Gauss_Curvature"}},
{1, {"Mean_Curvature"}},
{2, {"Gauss_Curvature"}},
{3, {"Mean_Curvature"}},
};
std::vector<std::string> txt{"Gauss_Curvature", "Mean_Curvature"};
auto txtPos = GetTextPositions(txt, VTK_TEXT_CENTERED, VTK_TEXT_BOTTOM, 0.45);
std::map<int, TTextPosition> namePositions = {
{0, {txtPos["Gauss_Curvature"]}},
{1, {txtPos["Mean_Curvature"]}},
{2, {txtPos["Gauss_Curvature"]}},
{3, {txtPos["Mean_Curvature"]}},
};
std::vector<vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>> actors;
std::vector<vtkSmartPointer<vtkTextWidget>> textWidgets;
std::vector<vtkSmartPointer<vtkScalarBarActor>> scalarBars;
std::vector<vtkSmartPointer<vtkScalarBarWidget>> sbWidgets;
std::vector<vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer>> renderers;
for (size_t idx = 0; idx < sources.size(); ++idx)
{
actors.push_back(vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New());
textWidgets.push_back(vtkSmartPointer<vtkTextWidget>::New());
scalarBars.push_back(vtkSmartPointer<vtkScalarBarActor>::New());
sbWidgets.push_back(vtkSmartPointer<vtkScalarBarWidget>::New());
renderers.push_back(vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer>::New());
}
// Create a common text property.
vtkNew<vtkTextProperty> textProp;
// textProp->SetFontFamilyToCourier();
textProp->SetFontSize(16);
textProp->SetVerticalJustificationToCentered();
textProp->SetJustificationToCentered();
textProp->BoldOn();
textProp->ItalicOn();
textProp->ShadowOn();
textProp->SetColor(colors->GetColor3d("LightGoldenrodYellow").GetData());
// auto lut = GetDivergingLut();
auto lut = GetDivergingLut1();
// Scalar bar properties.
auto sbProperties = ScalarBarProperties();
sbProperties.lut = lut;
sbProperties.orientation = true;
sbProperties.number_of_labels = 7;
// RenderWindow Dimensions
auto rendererSize = 512;
auto gridDimensions = 2;
auto windowWidth = rendererSize * gridDimensions;
vtkNew<vtkRenderWindow> renWin;
renWin->SetSize(rendererSize * gridDimensions, rendererSize * gridDimensions);
auto appFn = fs::path((app.get_name())).stem().string();
renWin->SetWindowName(appFn.c_str());
vtkNew<vtkRenderWindowInteractor> iRen;
iRen->SetRenderWindow(renWin);
vtkNew<vtkInteractorStyleTrackballCamera> style;
iRen->SetInteractorStyle(style);
// Add and position the renders in the render window.
for (auto row = 0; row < gridDimensions; ++row)
{
for (auto col = 0; col < gridDimensions; ++col)
{
auto idx = row * gridDimensions + col;
renderers[idx]->SetViewport(
static_cast<double>(col) / gridDimensions,
(static_cast<double>(gridDimensions) - (row + 1.0)) / gridDimensions,
(static_cast<double>(col) + 1) / gridDimensions,
(static_cast<double>(gridDimensions) - row) / gridDimensions);
renWin->AddRenderer(renderers[idx]);
renderers[idx]->AddActor(actors[idx]);
renderers[idx]->SetBackground(colors->GetColor3d("SlateGray").GetData());
}
}
for (auto idx = 0; idx < static_cast<int>(sources.size()); ++idx)
{
std::string curvatureName = curvatures[idx];
std::replace(curvatureName.begin(), curvatureName.end(), '_', ' ');
sources[idx]->GetPointData()->SetActiveScalars(curvatures[idx].c_str());
auto scalarRange = sources[idx]
->GetPointData()
->GetScalars(curvatures[idx].c_str())
->GetRange();
vtkNew<vtkPolyDataMapper> mapper;
mapper->SetInputData(sources[idx]);
mapper->SetScalarModeToUsePointFieldData();
mapper->SelectColorArray(curvatures[idx].c_str());
mapper->SetScalarRange(scalarRange);
mapper->SetLookupTable(lut);
actors[idx]->SetMapper(mapper);
vtkNew<vtkTextActor> textActor;
textActor->SetInput(curvatureName.c_str());
textActor->SetTextScaleModeToNone();
textActor->SetTextProperty(textProp);
auto pos = namePositions[idx];
vtkNew<vtkTextRepresentation> textRep;
textRep->EnforceNormalizedViewportBoundsOn();
textRep->SetPosition(pos["p"][0], pos["p"][1]);
textRep->SetPosition2(pos["p2"][0], pos["p2"][1]);
textWidgets[idx]->SetRepresentation(textRep);
textWidgets[idx]->SetTextActor(textActor);
textWidgets[idx]->SelectableOff();
textWidgets[idx]->ResizableOn();
// Create a scalar bar
std::string sbName = curvatures[idx];
std::replace(sbName.begin(), sbName.end(), '_', '\n');
sbProperties.titleText = sbName + '\n';
sbWidgets[idx] = MakeScalarBarWidget(sbProperties, textProp, textProp,
renderers[idx], iRen);
}
// Link the cameras.
for (auto row = 0; row < gridDimensions; ++row)
{
auto camera = renderers[row * gridDimensions]->GetActiveCamera();
for (auto col = 0; col < gridDimensions; ++col)
{
auto idx = row * gridDimensions + col;
if (idx != row * gridDimensions)
{
renderers[idx]->SetActiveCamera(camera);
}
}
renderers[row * gridDimensions]->ResetCamera();
}
for (auto row = 0; row < gridDimensions; ++row)
{
for (auto col = 0; col < gridDimensions; ++col)
{
auto idx = row * gridDimensions + col;
textWidgets[idx]->SetDefaultRenderer(renderers[idx]);
textWidgets[idx]->SetInteractor(iRen);
textWidgets[idx]->On();
}
}
renWin->Render();
iRen->Start();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
namespace {
void AdjustEdgeCurvatures(vtkPolyData* source, std::string const& curvatureName,
double const& epsilon)
{
auto PointNeighbourhood =
[&source](vtkIdType const& pId) -> std::set<vtkIdType> {
// Extract the topological neighbors for point pId. In two steps:
// 1) source->GetPointCells(pId, cellIds)
// 2) source->GetCellPoints(cellId, cellPointIds) for all cellId in cellIds
vtkNew<vtkIdList> cellIds;
source->GetPointCells(pId, cellIds);
std::set<vtkIdType> neighbours;
for (vtkIdType i = 0; i < cellIds->GetNumberOfIds(); ++i)
{
auto cellId = cellIds->GetId(i);
vtkNew<vtkIdList> cellPointIds;
source->GetCellPoints(cellId, cellPointIds);
for (vtkIdType j = 0; j < cellPointIds->GetNumberOfIds(); ++j)
{
neighbours.insert(cellPointIds->GetId(j));
}
}
return neighbours;
};
auto ComputeDistance = [&source](vtkIdType const& ptIdA,
vtkIdType const& ptIdB) {
std::array<double, 3> ptA{0.0, 0.0, 0.0};
std::array<double, 3> ptB{0.0, 0.0, 0.0};
std::array<double, 3> ptC{0.0, 0.0, 0.0};
source->GetPoint(ptIdA, ptA.data());
source->GetPoint(ptIdB, ptB.data());
std::transform(std::begin(ptA), std::end(ptA), std::begin(ptB),
std::begin(ptC), std::minus<double>());
// Calculate the norm.
auto result = std::sqrt(std::inner_product(std::begin(ptC), std::end(ptC),
std::begin(ptC), 0.0));
return result;
};
source->GetPointData()->SetActiveScalars(curvatureName.c_str());
// Curvature as a vector.
auto array = source->GetPointData()->GetAbstractArray(curvatureName.c_str());
std::vector<double> curvatures;
for (vtkIdType i = 0; i < source->GetNumberOfPoints(); ++i)
{
curvatures.push_back(array->GetVariantValue(i).ToDouble());
}
// Get the boundary point IDs.
std::string name = "Ids";
#ifdef USE_USE_GENERATE_IDS
vtkNew<vtkGenerateIds> idFilter;
#else
vtkNew<vtkIdFilter> idFilter;
#endif
idFilter->SetInputData(source);
idFilter->SetPointIds(true);
idFilter->SetCellIds(false);
idFilter->SetPointIdsArrayName(name.c_str());
idFilter->SetCellIdsArrayName(name.c_str());
idFilter->Update();
vtkNew<vtkFeatureEdges> edges;
edges->SetInputConnection(idFilter->GetOutputPort());
edges->BoundaryEdgesOn();
edges->ManifoldEdgesOff();
edges->NonManifoldEdgesOff();
edges->FeatureEdgesOff();
edges->Update();
auto edgeAarray =
edges->GetOutput()->GetPointData()->GetAbstractArray(name.c_str());
std::vector<vtkIdType> boundaryIds;
for (vtkIdType i = 0; i < edges->GetOutput()->GetNumberOfPoints(); ++i)
{
boundaryIds.push_back(edgeAarray->GetVariantValue(i).ToInt());
}
// Remove duplicate Ids.
std::set<vtkIdType> pIdsSet(boundaryIds.begin(), boundaryIds.end());
for (auto const pId : boundaryIds)
{
auto pIdsNeighbors = PointNeighbourhood(pId);
std::set<vtkIdType> pIdsNeighborsInterior;
std::set_difference(
pIdsNeighbors.begin(), pIdsNeighbors.end(), pIdsSet.begin(),
pIdsSet.end(),
std::inserter(pIdsNeighborsInterior, pIdsNeighborsInterior.begin()));
// Compute distances and extract curvature values.
std::vector<double> curvs;
std::vector<double> dists;
for (auto const pIdN : pIdsNeighborsInterior)
{
curvs.push_back(curvatures[pIdN]);
dists.push_back(ComputeDistance(pIdN, pId));
}
std::vector<vtkIdType> nonZeroDistIds;
for (size_t i = 0; i < dists.size(); ++i)
{
if (dists[i] > 0)
{
nonZeroDistIds.push_back(i);
}
}
std::vector<double> curvsNonZero;
std::vector<double> distsNonZero;
for (auto const i : nonZeroDistIds)
{
curvsNonZero.push_back(curvs[i]);
distsNonZero.push_back(dists[i]);
}
// Iterate over the edge points and compute the curvature as the weighted
// average of the neighbours.
auto countInvalid = 0;
auto newCurv = 0.0;
if (curvsNonZero.size() > 0)
{
std::vector<double> weights;
double sum = 0.0;
for (auto const d : distsNonZero)
{
sum += 1.0 / d;
weights.push_back(1.0 / d);
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < weights.size(); ++i)
{
weights[i] = weights[i] / sum;
}
newCurv = std::inner_product(curvsNonZero.begin(), curvsNonZero.end(),
weights.begin(), 0.0);
}
else
{
// Corner case.
// countInvalid += 1;
// Assuming the curvature of the point is planar.
newCurv = 0.0;
}
// Set the new curvature value.
curvatures[pId] = newCurv;
}
// Set small values to zero.
if (epsilon != 0.0)
{
auto eps = std::abs(epsilon);
for (size_t i = 0; i < curvatures.size(); ++i)
{
if (std::abs(curvatures[i]) < eps)
{
curvatures[i] = 0.0;
}
}
}
if (static_cast<size_t>(source->GetNumberOfPoints()) != curvatures.size())
{
std::string s = curvatureName;
s += ":\nCannot add the adjusted curvatures to the source.\n";
s += " The number of points in source does not equal the\n";
s += " number of point ids in the adjusted curvature array.";
std::cerr << s << std::endl;
return;
}
vtkNew<vtkDoubleArray> adjustedCurvatures;
adjustedCurvatures->SetName(curvatureName.c_str());
for (auto curvature : curvatures)
{
adjustedCurvatures->InsertNextTuple1(curvature);
}
source->GetPointData()->AddArray(adjustedCurvatures);
source->GetPointData()->SetActiveScalars(curvatureName.c_str());
}
// clang-format off
/**
* See: [Diverging Color Maps for Scientific Visualization](https://www.kennethmoreland.com/color-maps/)
*
* start point midPoint end point
* cool to warm: 0.230, 0.299, 0.754 0.865, 0.865, 0.865 0.706, 0.016, 0.150
* purple to orange: 0.436, 0.308, 0.631 0.865, 0.865, 0.865 0.759, 0.334, 0.046
* green to purple: 0.085, 0.532, 0.201 0.865, 0.865, 0.865 0.436, 0.308, 0.631
* blue to brown: 0.217, 0.525, 0.910 0.865, 0.865, 0.865 0.677, 0.492, 0.093
* green to red: 0.085, 0.532, 0.201 0.865, 0.865, 0.865 0.758, 0.214, 0.233
*
*/
// clang-format on
vtkSmartPointer<vtkLookupTable> GetDivergingLut()
{
vtkNew<vtkColorTransferFunction> ctf;
ctf->SetColorSpaceToDiverging();
ctf->AddRGBPoint(0.0, 0.230, 0.299, 0.754);
ctf->AddRGBPoint(0.5, 0.865, 0.865, 0.865);
ctf->AddRGBPoint(1.0, 0.706, 0.016, 0.150);
auto tableSize = 256;
vtkNew<vtkLookupTable> lut;
lut->SetNumberOfTableValues(tableSize);
lut->Build();
for (auto i = 0; i < lut->GetNumberOfColors(); ++i)
{
std::array<double, 3> rgb;
ctf->GetColor(static_cast<double>(i) / lut->GetNumberOfColors(),
rgb.data());
std::array<double, 4> rgba{0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0};
std::copy(std::begin(rgb), std::end(rgb), std::begin(rgba));
lut->SetTableValue(static_cast<vtkIdType>(i), rgba.data());
}
return lut;
}
vtkSmartPointer<vtkLookupTable> GetDivergingLut1()
{
vtkNew<vtkNamedColors> colors;
// Colour transfer function.
vtkNew<vtkColorTransferFunction> ctf;
ctf->SetColorSpaceToDiverging();
ctf->AddRGBPoint(0.0, colors->GetColor3d("MidnightBlue").GetRed(),
colors->GetColor3d("MidnightBlue").GetGreen(),
colors->GetColor3d("MidnightBlue").GetBlue());
ctf->AddRGBPoint(0.5, colors->GetColor3d("Gainsboro").GetRed(),
colors->GetColor3d("Gainsboro").GetGreen(),
colors->GetColor3d("Gainsboro").GetBlue());
ctf->AddRGBPoint(1.0, colors->GetColor3d("DarkOrange").GetRed(),
colors->GetColor3d("DarkOrange").GetGreen(),
colors->GetColor3d("DarkOrange").GetBlue());
// Lookup table.
vtkNew<vtkLookupTable> lut;
lut->SetNumberOfColors(256);
for (auto i = 0; i < lut->GetNumberOfColors(); ++i)
{
std::array<double, 3> rgb;
ctf->GetColor(double(i) / lut->GetNumberOfColors(), rgb.data());
std::array<double, 4> rgba{0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0};
std::copy(std::begin(rgb), std::end(rgb), std::begin(rgba));
lut->SetTableValue(i, rgba.data());
}
return lut;
}
vtkNew<vtkScalarBarWidget>
MakeScalarBarWidget(ScalarBarProperties& sbProperties,
vtkTextProperty* textProperty,
vtkTextProperty* labelTextProperty, vtkRenderer* ren,
vtkRenderWindowInteractor* iren)
{
vtkNew<vtkScalarBarActor> sbActor;
sbActor->SetLookupTable(sbProperties.lut);
sbActor->SetTitle(sbProperties.titleText.c_str());
sbActor->UnconstrainedFontSizeOn();
sbActor->SetNumberOfLabels(sbProperties.number_of_labels);
sbActor->SetTitleTextProperty(textProperty);
sbActor->SetLabelTextProperty(labelTextProperty);
sbActor->SetLabelFormat(sbProperties.labelFormat.c_str());
vtkNew<vtkScalarBarRepresentation> sbRep;
sbRep->EnforceNormalizedViewportBoundsOn();
sbRep->SetOrientation(sbProperties.orientation);
// Set the position.
sbRep->GetPositionCoordinate()->SetCoordinateSystemToNormalizedViewport();
sbRep->GetPosition2Coordinate()->SetCoordinateSystemToNormalizedViewport();
if (sbProperties.orientation)
{
auto p1 = sbProperties.positionV["p"];
auto p2 = sbProperties.positionV["p2"];
sbRep->GetPositionCoordinate()->SetValue(p1.data());
sbRep->GetPosition2Coordinate()->SetValue(p2.data());
}
else
{
auto p1 = sbProperties.positionH["p"];
auto p2 = sbProperties.positionH["p2"];
sbRep->GetPositionCoordinate()->SetValue(p1.data());
sbRep->GetPosition2Coordinate()->SetValue(p2.data());
}
vtkNew<vtkScalarBarWidget> widget;
widget->SetRepresentation(sbRep);
widget->SetScalarBarActor(sbActor);
widget->SetDefaultRenderer(ren);
widget->SetInteractor(iren);
widget->EnabledOn();
return widget;
}
TTextPositions GetTextPositions(std::vector<std::string> const& names,
int const justification,
int const vertical_justification,
double const width, double const height)
{
// The gap between the left or right edge of the screen and the text.
auto dx = 0.02;
auto w = abs(width);
if (w > 0.96)
{
w = 0.96;
}
auto y0 = 0.01;
auto h = abs(height);
if (h > 0.9)
{
h = 0.9;
}
auto dy = h;
if (vertical_justification == VTK_TEXT_TOP)
{
y0 = 1.0 - (dy + y0);
}
if (vertical_justification == VTK_TEXT_CENTERED)
{
y0 = 0.5 - (dy / 2.0 + y0);
}
auto minmaxIt =
std::minmax_element(names.begin(), names.end(),
[](const std::string& a, const std::string& b) {
return a.length() < b.length();
});
// auto nameLenMin = minmaxIt.first->size();
auto nameLenMax = minmaxIt.second->size();
TTextPositions textPositions;
for (const auto& k : names)
{
auto sz = k.size();
auto delta_sz = w * sz / nameLenMax;
if (delta_sz > w)
{
delta_sz = w;
}
double x0 = 0;
if (justification == VTK_TEXT_CENTERED)
{
x0 = 0.5 - delta_sz / 2.0;
}
else if (justification == VTK_TEXT_RIGHT)
{
x0 = 1.0 - dx - delta_sz;
}
else
{
// Default is left justification.
x0 = dx;
}
textPositions[k] = {{"p", {x0, y0}}, {"p2", {delta_sz, dy}}};
// For testing.
// std::cout << k << std::endl;
// std::cout << " p: " << textPositions[k]["p"][0] << ", "
// << textPositions[k]["p"][1] << std::endl;
// std::cout << " p2: " << textPositions[k]["p2"][0] << ", "
// << textPositions[k]["p2"][1] << std::endl;
}
return textPositions;
}
std::string Title(const std::string& input)
{
std::string result = input;
bool capitalizeNext = true;
for (char& c : result)
{
if (std::isspace(static_cast<unsigned char>(c)))
{
capitalizeNext = true;
}
else if (capitalizeNext)
{
c = static_cast<char>(std::toupper(static_cast<unsigned char>(c)));
capitalizeNext = false;
}
else
{
c = static_cast<char>(std::tolower(static_cast<unsigned char>(c)));
}
}
return result;
}
} // namespace
CMakeLists.txt¶
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.12 FATAL_ERROR)
project(CurvaturesDemo)
find_package(VTK COMPONENTS
CommonColor
CommonComputationalGeometry
CommonCore
CommonDataModel
CommonTransforms
FiltersCore
FiltersGeneral
FiltersSources
InteractionStyle
InteractionWidgets
RenderingAnnotation
RenderingContextOpenGL2
RenderingCore
RenderingFreeType
RenderingGL2PSOpenGL2
RenderingOpenGL2
cli11
fmt
)
if (NOT VTK_FOUND)
message(FATAL_ERROR "CurvaturesDemo: Unable to find the VTK build folder.")
endif()
# Prevent a "command line is too long" failure in Windows.
set(CMAKE_NINJA_FORCE_RESPONSE_FILE "ON" CACHE BOOL "Force Ninja to use response files.")
add_executable(CurvaturesDemo MACOSX_BUNDLE CurvaturesDemo.cxx )
target_link_libraries(CurvaturesDemo PRIVATE ${VTK_LIBRARIES}
)
# vtk_module_autoinit is needed
vtk_module_autoinit(
TARGETS CurvaturesDemo
MODULES ${VTK_LIBRARIES}
)
Download and Build CurvaturesDemo¶
Click here to download CurvaturesDemo and its CMakeLists.txt file. Once the tarball CurvaturesDemo.tar has been downloaded and extracted,
cd CurvaturesDemo/build
If VTK is installed:
cmake ..
If VTK is not installed but compiled on your system, you will need to specify the path to your VTK build:
cmake -DVTK_DIR:PATH=/home/me/vtk_build ..
Build the project:
make
and run it:
./CurvaturesDemo
WINDOWS USERS
Be sure to add the VTK bin directory to your path. This will resolve the VTK dll's at run time.