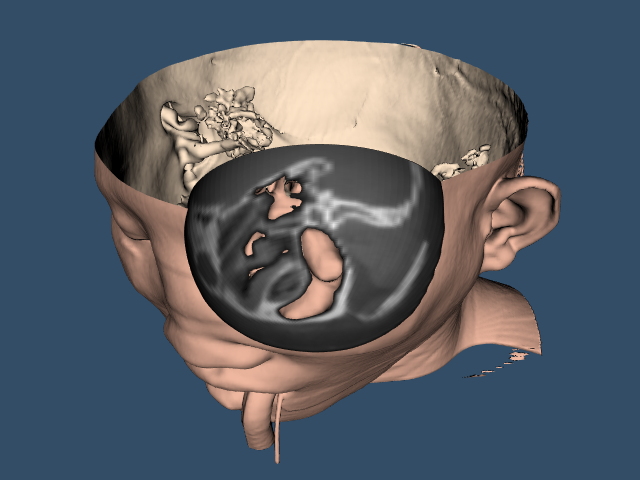
TissueLens
Repository source: TissueLens
Description¶
This example uses two vtkClipDataSet filters to achieve a "tissue lens" effect. First, a vtkSphere implicit function is used to clip a spherical hole in the isosurface extracted with vtkFlyingEdges3D or vtkMarchingCubes. Then a geometric vtkSphereSource samples the original volume data using a vtkProbeFilter. vtkClipDataSet uses the resulting scalar point data to clip the sphere surface with the isosurface value.
Usage
TissueLens FullHead.mhd
Note
The skin color was selected from Table 7 in Improvement of Haar Feature Based Face Detection in OpenCV Incorporating Human Skin Color Characteristic
Info
The example uses src/Testing/Data/FullHead.mhd which references src/Testing/Data/FullHead.raw.gz.
Other languages
See (Python)
Question
If you have a question about this example, please use the VTK Discourse Forum
Code¶
TissueLens.cxx
#include <vtkActor.h>
#include <vtkCamera.h>
#include <vtkClipDataSet.h>
#include <vtkDataSetMapper.h>
#include <vtkLookupTable.h>
#include <vtkMetaImageReader.h>
#include <vtkNamedColors.h>
#include <vtkNew.h>
#include <vtkProbeFilter.h>
#include <vtkProperty.h>
#include <vtkRenderWindow.h>
#include <vtkRenderWindowInteractor.h>
#include <vtkRenderer.h>
#include <vtkSphere.h>
#include <vtkSphereSource.h>
#include <vtkUnstructuredGrid.h>
#include <vtkVersion.h>
// vtkFlyingEdges3D was introduced in VTK >= 8.2
#if VTK_MAJOR_VERSION >= 9 || (VTK_MAJOR_VERSION >= 8 && VTK_MINOR_VERSION >= 2)
#define USE_FLYING_EDGES
#else
#undef USE_FLYING_EDGES
#endif
#ifdef USE_FLYING_EDGES
#include <vtkFlyingEdges3D.h>
#else
#include <vtkMarchingCubes.h>
#endif
#include <array>
#include <iostream>
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
vtkNew<vtkNamedColors> colors;
std::array<unsigned char, 4> skinColor{{240, 184, 160, 255}};
colors->SetColor("SkinColor", skinColor.data());
std::array<unsigned char, 4> backColor{{255, 229, 200, 255}};
colors->SetColor("BackfaceColor", backColor.data());
std::array<unsigned char, 4> bkg{{51, 77, 102, 255}};
colors->SetColor("BkgColor", bkg.data());
if (argc < 2)
{
std::cout << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " file.mhd e.g. FullHead.mhd" << endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// Read the volume data.
vtkNew<vtkMetaImageReader> reader;
reader->SetFileName(argv[1]);
reader->Update();
// An isosurface, or contour value of 500 is known to correspond to the
// skin of the patient.
#ifdef USE_FLYING_EDGES
vtkNew<vtkFlyingEdges3D> skinExtractor;
#else
vtkNew<vtkMarchingCubes> skinExtractor;
#endif
skinExtractor->SetInputConnection(reader->GetOutputPort());
skinExtractor->SetValue(0, 500);
// Define a spherical clip function to clip the isosurface.
vtkNew<vtkSphere> clipFunction;
clipFunction->SetRadius(50);
clipFunction->SetCenter(73, 52, 15);
// Clip the isosurface with a sphere.
vtkNew<vtkClipDataSet> skinClip;
skinClip->SetInputConnection(skinExtractor->GetOutputPort());
skinClip->SetClipFunction(clipFunction);
skinClip->SetValue(0);
skinClip->GenerateClipScalarsOn();
skinClip->Update();
vtkNew<vtkDataSetMapper> skinMapper;
skinMapper->SetInputConnection(skinClip->GetOutputPort());
skinMapper->ScalarVisibilityOff();
vtkNew<vtkActor> skin;
skin->SetMapper(skinMapper);
skin->GetProperty()->SetDiffuseColor(
colors->GetColor3d("SkinColor").GetData());
vtkNew<vtkProperty> backProp;
backProp->SetDiffuseColor(colors->GetColor3d("BackfaceColor").GetData());
skin->SetBackfaceProperty(backProp);
// Define a model for the "lens". Its geometry matches the implicit
// sphere used to clip the isosurface.
vtkNew<vtkSphereSource> lensModel;
lensModel->SetRadius(50);
lensModel->SetCenter(73, 52, 15);
lensModel->SetPhiResolution(201);
lensModel->SetThetaResolution(101);
// Sample the input volume with the lens model geometry.
vtkNew<vtkProbeFilter> lensProbe;
lensProbe->SetInputConnection(lensModel->GetOutputPort());
lensProbe->SetSourceConnection(reader->GetOutputPort());
// Clip the lens data with the isosurface value.
vtkNew<vtkClipDataSet> lensClip;
lensClip->SetInputConnection(lensProbe->GetOutputPort());
lensClip->SetValue(500);
lensClip->GenerateClipScalarsOff();
lensClip->Update();
// Define a suitable grayscale lut.
vtkNew<vtkLookupTable> bwLut;
bwLut->SetTableRange(0, 2048);
bwLut->SetSaturationRange(0, 0);
bwLut->SetHueRange(0, 0);
bwLut->SetValueRange(0.2, 1);
bwLut->Build();
vtkNew<vtkDataSetMapper> lensMapper;
lensMapper->SetInputConnection(lensClip->GetOutputPort());
lensMapper->SetScalarRange(lensClip->GetOutput()->GetScalarRange());
lensMapper->SetLookupTable(bwLut);
vtkNew<vtkActor> lens;
lens->SetMapper(lensMapper);
// It is convenient to create an initial view of the data. The FocalPoint
// and Position form a vector direction. Later on (ResetCamera() method)
// this vector is used to position the camera to look at the data in
// this direction.
vtkNew<vtkCamera> aCamera;
aCamera->SetViewUp(0, 0, -1);
aCamera->SetPosition(0, -1, 0);
aCamera->SetFocalPoint(0, 0, 0);
aCamera->ComputeViewPlaneNormal();
aCamera->Azimuth(30.0);
aCamera->Elevation(30.0);
// Create the renderer, the render window, and the interactor. The renderer
// draws into the render window, the interactor enables mouse- and
// keyboard-based interaction with the data within the render window.
//
vtkNew<vtkRenderer> aRenderer;
vtkNew<vtkRenderWindow> renWin;
renWin->AddRenderer(aRenderer);
vtkNew<vtkRenderWindowInteractor> iren;
iren->SetRenderWindow(renWin);
// Actors are added to the renderer. An initial camera view is created.
// The Dolly() method moves the camera towards the FocalPoint,
// thereby enlarging the image.
aRenderer->AddActor(lens);
aRenderer->AddActor(skin);
aRenderer->SetActiveCamera(aCamera);
aRenderer->ResetCamera();
aCamera->Dolly(1.5);
// Set a background color for the renderer and set the size of the
// render window (expressed in pixels).
aRenderer->SetBackground(colors->GetColor3d("BkgColor").GetData());
renWin->SetSize(640, 480);
renWin->SetWindowName("TissueLens");
// Note that when camera movement occurs (as it does in the Dolly()
// method), the clipping planes often need adjusting. Clipping planes
// consist of two planes: near and far along the view direction. The
// near plane clips out objects in front of the plane; the far plane
// clips out objects behind the plane. This way only what is drawn
// between the planes is actually rendered.
aRenderer->ResetCameraClippingRange();
// Initialize the event loop and then start it.
renWin->Render();
iren->Initialize();
iren->Start();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
CMakeLists.txt¶
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.12 FATAL_ERROR)
project(TissueLens)
find_package(VTK COMPONENTS
CommonColor
CommonCore
CommonDataModel
FiltersCore
FiltersGeneral
FiltersSources
IOImage
InteractionStyle
RenderingContextOpenGL2
RenderingCore
RenderingFreeType
RenderingGL2PSOpenGL2
RenderingOpenGL2
)
if (NOT VTK_FOUND)
message(FATAL_ERROR "TissueLens: Unable to find the VTK build folder.")
endif()
# Prevent a "command line is too long" failure in Windows.
set(CMAKE_NINJA_FORCE_RESPONSE_FILE "ON" CACHE BOOL "Force Ninja to use response files.")
add_executable(TissueLens MACOSX_BUNDLE TissueLens.cxx )
target_link_libraries(TissueLens PRIVATE ${VTK_LIBRARIES}
)
# vtk_module_autoinit is needed
vtk_module_autoinit(
TARGETS TissueLens
MODULES ${VTK_LIBRARIES}
)
Download and Build TissueLens¶
Click here to download TissueLens and its CMakeLists.txt file. Once the tarball TissueLens.tar has been downloaded and extracted,
cd TissueLens/build
If VTK is installed:
cmake ..
If VTK is not installed but compiled on your system, you will need to specify the path to your VTK build:
cmake -DVTK_DIR:PATH=/home/me/vtk_build ..
Build the project:
make
and run it:
./TissueLens
WINDOWS USERS
Be sure to add the VTK bin directory to your path. This will resolve the VTK dll's at run time.